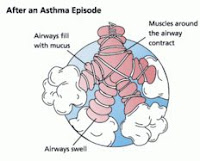
 The small airways of the lungs are rather inaccessible, which makes it difficult to study their responses to environmental exposure. Exhaled breath contains particles of respiratory tract lining fluid from the small airways. The particles are formed when closed airways open during inhalation. The researchers from Sweden have developed a method called Particles in Exhaled air (PExA®) to measure and sample these particles in the exhaled aerosol. They studied the effects of birch pollen exposure on the small airways of individuals with asthma and birch pollen allergy.
The small airways of the lungs are rather inaccessible, which makes it difficult to study their responses to environmental exposure. Exhaled breath contains particles of respiratory tract lining fluid from the small airways. The particles are formed when closed airways open during inhalation. The researchers from Sweden have developed a method called Particles in Exhaled air (PExA®) to measure and sample these particles in the exhaled aerosol. They studied the effects of birch pollen exposure on the small airways of individuals with asthma and birch pollen allergy. The amount of exhaled particles was reduced after birch pollen exposure in subjects with asthma and birch pollen allergy. The reduction in the number of exhaled particles may be due to inflammation in the small airways, which would reduce their diameter and potentially reduce the number of small airways that open and close during inhalation and exhalation.
References:
Exhaled particles as markers of small airway inflammation in subjects with asthma. Larsson P et al. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2015 Dec 9. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12323. [Epub ahead of print] (free full text).
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/cpf.12323/full
The World Allergy Organization (WAO) Small Airways Working Group publishes a monthly "What's New?" summary and I have served as its editor since 2011. The summary features the top 3 asthma/small airways articles each month. The article above is a part of the project. The archive is here: http://www.worldallergy.org/small_airways_group/reviews/archive.php
Image source: Image source: FDA and Wikipedia, public domain.