Drug allergic reactions to immunosuppressants
The modern dermatologic armamentarium consists of a spectrum of T-cell immunosuppressant drugs, such as macrolides (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, sirolimus), dapsone, mycophenolate mofetil, and monoclonal antibodies. Dermatologic immunosuppressant drugs, such as macrolides (eg, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, and sirolimus), dapsone, and mycophenolate mofetil, have been reported to cause drug allergic reactions in addition to their known predictable adverse reactions.
CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil)

Mycophenolic acid. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
CellCept is available in multiple formulations: Capsules, Tablets, Oral Suspension, IV.
Allergic reactions to CellCept have been observed; therefore, CellCept is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid or any component of the drug product. CellCept Intravenous is contraindicated in patients who
are allergic to Polysorbate 80 (TWEEN).
Urticaria and a severe papulosquamous skin eruption have been reported after use of CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil).
There is no validated protocol for CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil) skin testing.
General info about skin tests in drug allergy
The sensitivity of skin tests appears to be moderate to high for immediate hypersensitivity reactions to betalactam antibiotics, perioperative drugs, heparins, platinum salts, radiocontrast media, but low for many other drugs (moderate/weak).
The parenteral preparation of the suspected drug, preferably the intravenous form at the recommended concentration, should be used for SPT and IDT. For drugs suspected of causing severe reactions or where literature/experience is lacking, skin tests should use nonirritant concentrations of the drug. This can be established using different dilutions of increasing drug concentration. The nonirritant drug concentration should ideally be established in healthy controls. Where the drug is available only in tablet, capsule or topical form, only SPT and/or patch test can be performed (moderate/strong).
There are no standardized protocols or data on the optimal drug concentration available for skin testing using drug solution prepared from an oral formulation (moderate/weak). The common practice is to dissolve the tablet/capsule content in 0.9% saline and use the maximum concentration achievable to make the test as sensitive as possible.
A positive skin test to nonirritating drug concentrations is consistent with an allergic mechanism, although the precise test accuracy (sensitivity/specificity) remains unknown (high/strong).
Fatal systemic anaphylaxis has been reported after IDT without preceding SPT. Intradermal test has a high sensitivity, but also a higher risk of inducing irritant reactions and false-positive results.
Drug challenge is needed
Because of limited sensitivity, a negative skin test does not rule out drug hypersensitivity (high/strong). Before re-administration, a drug provocation test is necessary.
Chemotherapeutic drugs
Except for platinum salts, an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs has not been demonstrated (moderate/strong).
Skin tests are useful for platinum salt-related immediate hypersensitivity reactions (moderate/strong) [50], while for other chemotherapeutic drugs, experience is limited and test results often negative (low/weak).
The irritant potential of chemotherapeutic drugs appears to be low. For platinum salts, the use of undiluted drugs is recommended (high/strong). For other chemotherapeutic drugs, SPT with undiluted agents is probably nonirritant, but due to toxicity concerns, a general recommendation cannot be given.
For IDT, a 1/10 dilution of most chemotherapeutic drugs is nonirritant and may be used in clinical practice (moderate/strong), whereas higher concentrations appear to be irritant (MP, personal communication; low/weak).
How do to a skin test for suspected drug allergy to CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil)?
A skin prick test with 1:1000, 1:100, 1:10 and 1:1 concentrations can be done. If this is negative, an IDT test with 1:1000 and 1:100 and 1:10 can be done. If this is negative, an oral challenge is recommended.
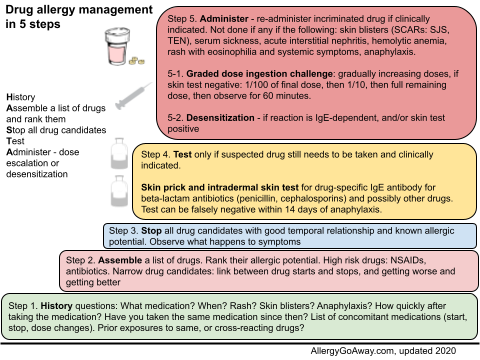
Drug allergy management in 5 steps (click to enlarge the image).
References:
CellCept® (mycophenolate mofetil) Information http://buff.ly/1NR9B5q
Prescribing info (PDF) http://www.gene.com/download/pdf/cellcept_prescribing.pdf
Levin N, Mali A, Karussis D. Severe skin reaction related to mycophenolate mofetil for myasthenia gravis. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005; 28:152–153. III. http://buff.ly/1NRcALb
Szyper-Kravitz M, Sheinberg P, Sidi Y, et al. Hypersensitivity to mycophenolate mofetil in systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnostic measures and successful desensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005;138:334 –336. III https://www.karger.com/Article/Pdf/88873
Drug Allergy: An Updated Practice Parameter. AAAAI (PDF) http://buff.ly/1gUxkVp
Skin test concentrations for systemically administered drugs – an ENDA/EAACI Drug Allergy Interest Group position paper. Allergy, 2013.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1111/all.12142/
The modern dermatologic armamentarium consists of a spectrum of T-cell immunosuppressant drugs, such as macrolides (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, sirolimus), dapsone, mycophenolate mofetil, and monoclonal antibodies. Dermatologic immunosuppressant drugs, such as macrolides (eg, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, and sirolimus), dapsone, and mycophenolate mofetil, have been reported to cause drug allergic reactions in addition to their known predictable adverse reactions.
CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil)

Mycophenolic acid. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
CellCept is available in multiple formulations: Capsules, Tablets, Oral Suspension, IV.
Allergic reactions to CellCept have been observed; therefore, CellCept is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid or any component of the drug product. CellCept Intravenous is contraindicated in patients who
are allergic to Polysorbate 80 (TWEEN).
Urticaria and a severe papulosquamous skin eruption have been reported after use of CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil).
There is no validated protocol for CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil) skin testing.
General info about skin tests in drug allergy
The sensitivity of skin tests appears to be moderate to high for immediate hypersensitivity reactions to betalactam antibiotics, perioperative drugs, heparins, platinum salts, radiocontrast media, but low for many other drugs (moderate/weak).
The parenteral preparation of the suspected drug, preferably the intravenous form at the recommended concentration, should be used for SPT and IDT. For drugs suspected of causing severe reactions or where literature/experience is lacking, skin tests should use nonirritant concentrations of the drug. This can be established using different dilutions of increasing drug concentration. The nonirritant drug concentration should ideally be established in healthy controls. Where the drug is available only in tablet, capsule or topical form, only SPT and/or patch test can be performed (moderate/strong).
There are no standardized protocols or data on the optimal drug concentration available for skin testing using drug solution prepared from an oral formulation (moderate/weak). The common practice is to dissolve the tablet/capsule content in 0.9% saline and use the maximum concentration achievable to make the test as sensitive as possible.
A positive skin test to nonirritating drug concentrations is consistent with an allergic mechanism, although the precise test accuracy (sensitivity/specificity) remains unknown (high/strong).
Fatal systemic anaphylaxis has been reported after IDT without preceding SPT. Intradermal test has a high sensitivity, but also a higher risk of inducing irritant reactions and false-positive results.
Drug challenge is needed
Because of limited sensitivity, a negative skin test does not rule out drug hypersensitivity (high/strong). Before re-administration, a drug provocation test is necessary.
Chemotherapeutic drugs
Except for platinum salts, an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs has not been demonstrated (moderate/strong).
Skin tests are useful for platinum salt-related immediate hypersensitivity reactions (moderate/strong) [50], while for other chemotherapeutic drugs, experience is limited and test results often negative (low/weak).
The irritant potential of chemotherapeutic drugs appears to be low. For platinum salts, the use of undiluted drugs is recommended (high/strong). For other chemotherapeutic drugs, SPT with undiluted agents is probably nonirritant, but due to toxicity concerns, a general recommendation cannot be given.
For IDT, a 1/10 dilution of most chemotherapeutic drugs is nonirritant and may be used in clinical practice (moderate/strong), whereas higher concentrations appear to be irritant (MP, personal communication; low/weak).
How do to a skin test for suspected drug allergy to CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil)?
A skin prick test with 1:1000, 1:100, 1:10 and 1:1 concentrations can be done. If this is negative, an IDT test with 1:1000 and 1:100 and 1:10 can be done. If this is negative, an oral challenge is recommended.
Drug allergy management in 5 steps (click to enlarge the image).
References:
CellCept® (mycophenolate mofetil) Information http://buff.ly/1NR9B5q
Prescribing info (PDF) http://www.gene.com/download/pdf/cellcept_prescribing.pdf
Levin N, Mali A, Karussis D. Severe skin reaction related to mycophenolate mofetil for myasthenia gravis. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005; 28:152–153. III. http://buff.ly/1NRcALb
Szyper-Kravitz M, Sheinberg P, Sidi Y, et al. Hypersensitivity to mycophenolate mofetil in systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnostic measures and successful desensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005;138:334 –336. III https://www.karger.com/Article/Pdf/88873
Drug Allergy: An Updated Practice Parameter. AAAAI (PDF) http://buff.ly/1gUxkVp
Skin test concentrations for systemically administered drugs – an ENDA/EAACI Drug Allergy Interest Group position paper. Allergy, 2013.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1111/all.12142/