What is soy lecithin?
Soy lecithin is a fatty derivative of soy. It is present in many foods. Soy lecithin contains a trace amount of detectable soy protein. Lecithin is a generic term to designate any group of fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues composed of phosphoric acid, choline, fatty acids, glycerol, glycolipids, triglycerides, and phospholipids. There is no protein in lecithin. Most food allergies are to protein antigens.

8 foods cause 90% of food allergies (click to enlarge the image). The likelihood of a negative oral food challenge is shown in relation to the respective values of skin prick test (SPT) and serum IgE (sIgE).
Soy lecithin in foods
The FDA exempts highly refined soybean oil from being labeled as an allergen. Studies show most allergic individuals can safely eat soy oil that has been highly refined (not cold pressed, expeller pressed, or extruded soybean oil). Similar caution applies to peanut oil.
Most individuals allergic to soy can safely eat soy lecithin. If there are any doubts, a food challenge in the allergy clinic can be considered.
Soy lecithin in medications
Soy lecithin is also present in certain inhalers and propofol. The product insert on some of these medications indicates a contraindication for the use of products with soy lecithin if there is an allergy to soybean or peanut. However, the degree of risk for use of soy-lecithin containing medications in persons with peanut or soy allergy has not been systematically evaluated. Considering the small amount of protein present, the risk of a reaction from these medications seems very low.
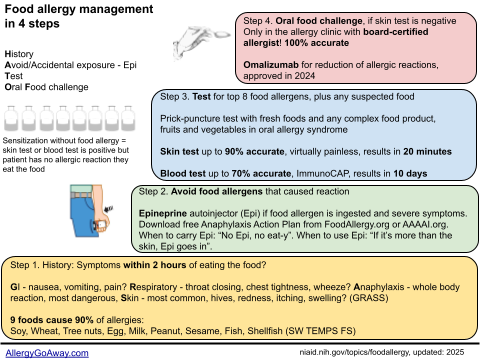
Food allergy management in 4 steps (click to enlarge the image).
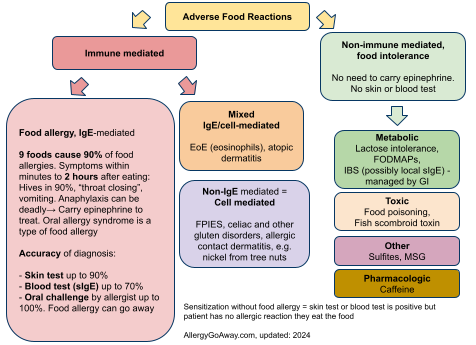
Adverse Food Reactions (click to enlarge the image).
References:
Safety of ingestion of soy oil and soy lecithin in patients with soy allergy. AAAAI Ask the Expert, 2011.
http://www.aaaai.org/ask-the-expert/safety-of-ingestion-soy-oil-and-soy-lecithin.aspx
Management of food allergy: Avoidance. UpToDate, 2014 http://buff.ly/1eMonGK
Soy lecithin is a fatty derivative of soy. It is present in many foods. Soy lecithin contains a trace amount of detectable soy protein. Lecithin is a generic term to designate any group of fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues composed of phosphoric acid, choline, fatty acids, glycerol, glycolipids, triglycerides, and phospholipids. There is no protein in lecithin. Most food allergies are to protein antigens.
8 foods cause 90% of food allergies (click to enlarge the image). The likelihood of a negative oral food challenge is shown in relation to the respective values of skin prick test (SPT) and serum IgE (sIgE).
Soy lecithin in foods
The FDA exempts highly refined soybean oil from being labeled as an allergen. Studies show most allergic individuals can safely eat soy oil that has been highly refined (not cold pressed, expeller pressed, or extruded soybean oil). Similar caution applies to peanut oil.
Most individuals allergic to soy can safely eat soy lecithin. If there are any doubts, a food challenge in the allergy clinic can be considered.
Soy lecithin in medications
Soy lecithin is also present in certain inhalers and propofol. The product insert on some of these medications indicates a contraindication for the use of products with soy lecithin if there is an allergy to soybean or peanut. However, the degree of risk for use of soy-lecithin containing medications in persons with peanut or soy allergy has not been systematically evaluated. Considering the small amount of protein present, the risk of a reaction from these medications seems very low.
Food allergy management in 4 steps (click to enlarge the image).
Adverse Food Reactions (click to enlarge the image).
References:
Safety of ingestion of soy oil and soy lecithin in patients with soy allergy. AAAAI Ask the Expert, 2011.
http://www.aaaai.org/ask-the-expert/safety-of-ingestion-soy-oil-and-soy-lecithin.aspx
Management of food allergy: Avoidance. UpToDate, 2014 http://buff.ly/1eMonGK