What is it?
Aspergillus niger is a cosmopolitan fungus and perhaps the most abundant species of Aspergillus. The name niger is from Latin, black, and aspergillum, a handled sphere for dispersing water, descriptive of the brown-black conidiophore.
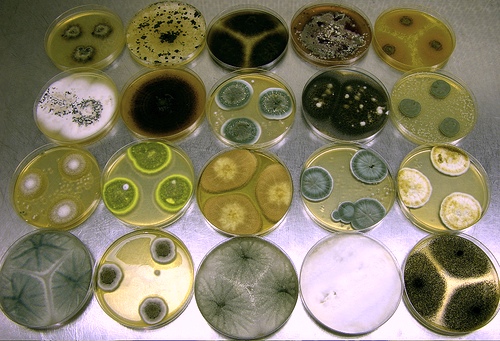
Various fungi including Penicillium and Aspergillus spp. growing in axenic culture. Image source: Wikipedia, Dr. David Midgley Cultures: Dr. David Midgley University of Sydney, Australia, Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.5 License.
Where is the fungus found?
Aspergillus niger is isolated from:
- house dust
- soil
- plant litter
- dried fruits
- nuts and seeds
- untreated textiles such as jute, hemp and cotton bracts
- thorns of rose bushes
Aspergillus niger damages foods such as stored fruits and vegetables, nuts and corn, oil seeds, grains, and dairy products.
Commercial use
This hard working fungus is used commercially. Aspergillus niger is industrially important since it decomposes plastic and cellulose.
It is used commercially in the degradation of organic waste such as squeeze remains from apple, potato garbage, sugar beet wastewater, in beer production, and in the production of organic acids and enzymes.
Clinical significance
Aspergillus niger is a common environmental allergen that plays a role in allergic rhinitis and asthma. It can also cause invasive disease in immunosuppressed patients.
References:
On The Cover – Aspergillus niger. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Volume 107, Issue 3, Page A11 (September 2011).
Aspergillus niger is a cosmopolitan fungus and perhaps the most abundant species of Aspergillus. The name niger is from Latin, black, and aspergillum, a handled sphere for dispersing water, descriptive of the brown-black conidiophore.

Various fungi including Penicillium and Aspergillus spp. growing in axenic culture. Image source: Wikipedia, Dr. David Midgley Cultures: Dr. David Midgley University of Sydney, Australia, Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.5 License.
Where is the fungus found?
Aspergillus niger is isolated from:
- house dust
- soil
- plant litter
- dried fruits
- nuts and seeds
- untreated textiles such as jute, hemp and cotton bracts
- thorns of rose bushes
Aspergillus niger damages foods such as stored fruits and vegetables, nuts and corn, oil seeds, grains, and dairy products.
Commercial use
This hard working fungus is used commercially. Aspergillus niger is industrially important since it decomposes plastic and cellulose.
It is used commercially in the degradation of organic waste such as squeeze remains from apple, potato garbage, sugar beet wastewater, in beer production, and in the production of organic acids and enzymes.
Clinical significance
Aspergillus niger is a common environmental allergen that plays a role in allergic rhinitis and asthma. It can also cause invasive disease in immunosuppressed patients.
References:
On The Cover – Aspergillus niger. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Volume 107, Issue 3, Page A11 (September 2011).