 Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) is an important treatment modality in patients with humoral or B-cell immune deficiency as replacement therapy. Soon after its introduction in the early 1980s for the treatment of patients with immune deficiency, IVIG was used in the treatment of children with idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP).
Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) is an important treatment modality in patients with humoral or B-cell immune deficiency as replacement therapy. Soon after its introduction in the early 1980s for the treatment of patients with immune deficiency, IVIG was used in the treatment of children with idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP).A lot more IVIG is used for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders than as replacement therapy in patients with immune deficiency.
A number of mechanisms for the immune modulation and anti-inflammatory actions of IVIG have been described:
- Fc receptor blockade
- inhibition of complement deposition
- enhancement of regulatory T cells (T regs)
- inhibition or neutralization of cytokines and growth factors
- accelerated clearance of autoantibodies
- modulation of adhesion molecules and cell receptors
- activation of regulatory macrophages through the FcγRIIb receptor
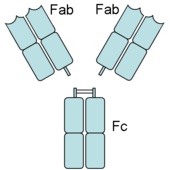
An antibody has Fab (fragment, antigen-binding) and Fc (fragment, crystalizable) regions. Fc receptors bind to the Fc region. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
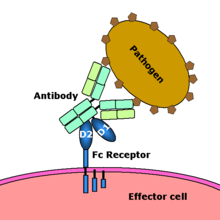
Fc receptor interaction with an antibody-coated microbial pathogen. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
IVIG affects many different pathways to modulate the immune and inflammatory response.
References:
The IgG molecule as a biological immune response modifier: Mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. Ballow M. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Dec 23.
Image source: OpenClipArt.org, public domain.