Respiratory exposure to a wide range of fungal spores and fragments is almost constant and 189 fungal species are thought to produce allergens.
Many fungi are capable of causing IgE-mediated hypersensitivity in humans. However, the most predominant fungi implicated in allergy belong to the genera Aspergillus, Alternaria, Cladosporium, and Penicillium.
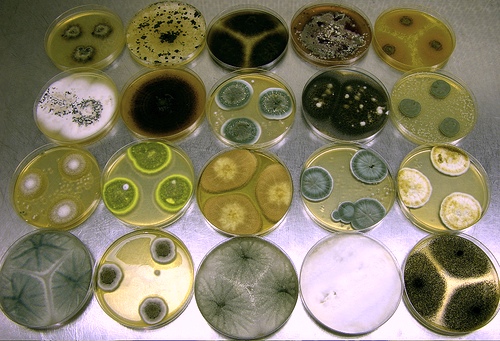
Various fungi including Penicillium and Aspergillus spp. growing in axenic culture. Image source:Wikipedia, Dr. David Midgley Cultures: Dr. David Midgley University of Sydney, Australia, Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.5 License.
Reviews of allergen sensitization conducted in geographically diverse areas suggest the most common causes of fungal sensitization in populations are Aspergillus, Alternaria and Cladosporium spp. These genera together with Penicillium are frequently among the most common fungi encountered in surveys of airborne fungi in indoor and outdoor environments worldwide.
A recent survey of spore levels in the UK suggests that the combined level of Aspergillus, Penicillium, Alternaria and Cladosporium spores forms approximately 15% of the total airborne fungal matter, much of the rest of which is accounted for by ascospores and basidiomycetes.
References:
Comparative genomics of fungal allergens and epitopes shows widespread distribution of closely related allergen and epitope orthologues. BMC Genomics 2006, 7:251doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-251.
Many fungi are capable of causing IgE-mediated hypersensitivity in humans. However, the most predominant fungi implicated in allergy belong to the genera Aspergillus, Alternaria, Cladosporium, and Penicillium.

Various fungi including Penicillium and Aspergillus spp. growing in axenic culture. Image source:Wikipedia, Dr. David Midgley Cultures: Dr. David Midgley University of Sydney, Australia, Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.5 License.
Reviews of allergen sensitization conducted in geographically diverse areas suggest the most common causes of fungal sensitization in populations are Aspergillus, Alternaria and Cladosporium spp. These genera together with Penicillium are frequently among the most common fungi encountered in surveys of airborne fungi in indoor and outdoor environments worldwide.
A recent survey of spore levels in the UK suggests that the combined level of Aspergillus, Penicillium, Alternaria and Cladosporium spores forms approximately 15% of the total airborne fungal matter, much of the rest of which is accounted for by ascospores and basidiomycetes.
References:
Comparative genomics of fungal allergens and epitopes shows widespread distribution of closely related allergen and epitope orthologues. BMC Genomics 2006, 7:251doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-251.