Using your Metered Dose Inhaler
Using your Spacer
Using Your Accuhaler/Advair Diskus
Using your Turbuhaler
Using your Autohaler
Related:
Proper techniques for the administration of inhaled medications to treat asthma - AAAAI - Ask the Expert, 2011.


 Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.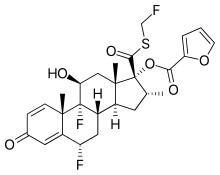

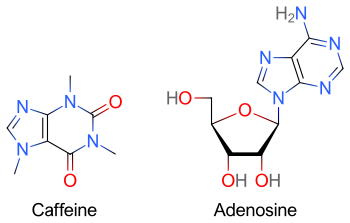



 Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.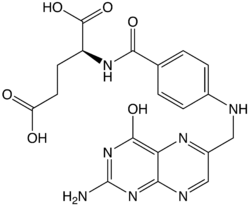
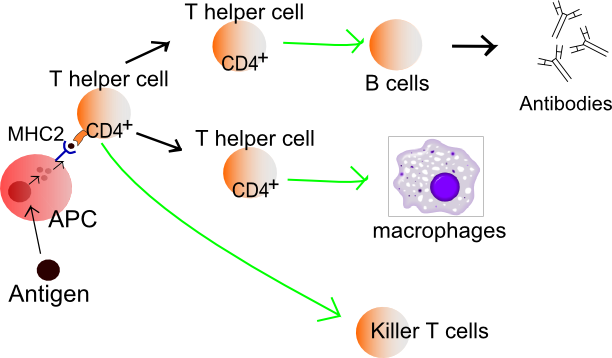



 Suboptimal adherence to inhaled steroids (ICS) is a known problem in children and adolescents, even when medications are administered under parental supervision. Poor adherence to asthma medications (less than 80%) was seen in 75% of children (JACI, 2011).
Suboptimal adherence to inhaled steroids (ICS) is a known problem in children and adolescents, even when medications are administered under parental supervision. Poor adherence to asthma medications (less than 80%) was seen in 75% of children (JACI, 2011). Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.


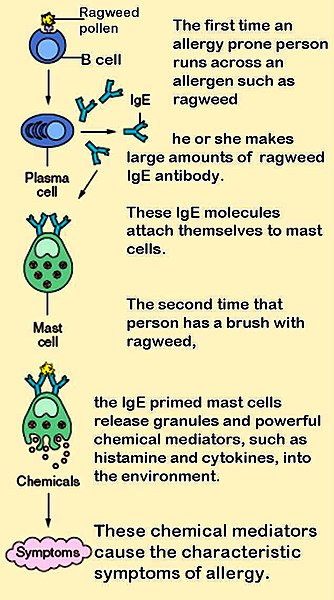
 Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day. Atopic dermatitis (AD) has been associated with an increased risk of lymphoma.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) has been associated with an increased risk of lymphoma.
 Once allergy has been ruled out, most patients with nonallergic rhinitis (NAR) are not followed up in allergy clinics, despite the persistence of rhinitis symptoms.
Once allergy has been ruled out, most patients with nonallergic rhinitis (NAR) are not followed up in allergy clinics, despite the persistence of rhinitis symptoms. Stress is known to worsen the course of asthma, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood.
Stress is known to worsen the course of asthma, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Maternal farm exposure decreases the risk of allergic disease in the offspring.
Maternal farm exposure decreases the risk of allergic disease in the offspring.
 Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
Health News of the Day is a daily summary made from the selected links I post on Twitter. It is in a bullet points format with links to the original sources which include 350 RSS feeds that produce about 2,500 items per day.
 Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of the monoclonal anti-IgE antibody omalizumab (Xolair) in treating patients with asthma. Omalizumab binds to Cε3 region of IgE.
Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of the monoclonal anti-IgE antibody omalizumab (Xolair) in treating patients with asthma. Omalizumab binds to Cε3 region of IgE.  Varraso and colleagues analyzed dietary and asthma data from more than 1000 French women with asthma.
Varraso and colleagues analyzed dietary and asthma data from more than 1000 French women with asthma.