 Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction occurs in many children with asthma. According to a Polish study, the best therapy for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children with asthma was budesonide plus montelukast or montelukast alone.
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction occurs in many children with asthma. According to a Polish study, the best therapy for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children with asthma was budesonide plus montelukast or montelukast alone.This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study compared different antiasthmatic treatments to protect patients (aged 6 to 18 years) from exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
A teadmill exercise challenge was performed before and after treatment. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction protection improved in the budesonide + montelukast and montelukast groups compared with other therapeutic options (budesonide + formoterol, budesonide alone and placebo).
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists (LTRA)
Antagonists of the CysLT1 receptor (LTRA) are efficacious as controller therapy in asthma and montelukast is FDA-approved for treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis.
Mast cells quickly generate different mediators from the metabolism of arachidonic acid: leukotrienes and prostglandins (LTC4, LTB4, PGD2). These substances are produced within minutes of IgE-receptor crosslinking on the surface of mast cells.

Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by oxygenation of 20-carbon essential fatty acids. There are 4 families of eicosanoids (PP-LT): prostaglandins (PG), prostacyclins (PGI), leukotrienes (LT) and thromboxanes (TX).

Mast cell mediators including (PP-LT): prostaglandins (PG), prostacyclins (PGI), leukotrienes (LT) and thromboxanes (TX). See more Allergy and Immunology mind maps here.
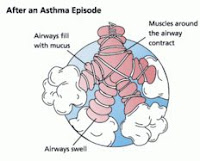
Exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB) (click to enlarge the image):
References:
Effect of different antiasthmatic treatments on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children with asthma. Iwona Stelmach et al. JACI, Volume 121, Issue 2, Pages 383-389 (February 2008).
Mast Cells and Basophils. Allergy Cases.
Pathogenesis of Asthma. Allergy Cases.
49-year-old man with childhood asthma who was told he would never be able to do exercise runs a marathon every day for a year. CNN, 2011.
Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.