Approximately 5% to 10% of patients with asthma have severe disease that is refractory or unresponsive to inhaled corticosteroids (ICS).
What are some of the treatment options for such patients?
- Anti-IgE. Omalizumab (Xolair). Omalizumab binds to Cε3 region of IgE. Oral corticosteroids were withdrawn in 74% of severe asthma patients treated with omalizumab - Current Medical Research and Opinion, 2010.
- Anti-TNF-α
Etanercept (Enbrel)
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a proinflammatory cytokine that has been implicated in the airway pathology in asthma. TNF-α may play an important role in severe refractory asthma.
Preliminary studies with anti–TNF-α therapy look promising but there is a marked heterogeneity in response, suggesting that benefit is likely to be reserved to a small subgroup. The long-term safety of anti–TNF-α therapy is also uncertain.
Etanercept (Enbrel) is a recombinant human TNF-α receptor fusion protein (anti-TNF-α). Its therapeutic potential is based on the fact that TNF-alpha is the "master regulator" of the inflammatory response in many organ systems.
Etanercept is a large molecule that binds to TNF-α and decreases its role in disorders involving excess inflammation such as:
- ankylosing spondylitis
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- psoriasis
- psoriatic arthritis

Mediators from Eosinophils. TNF-α is one of them.
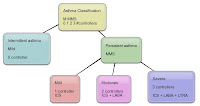
Asthma classification and treatment for each stage. See more Allergy and Immunology mind maps here.

Severe asthma - differential diagnosis and management (click to enlarge the image).
References:
Targeting TNF-α: A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. JACI, Volume 121, Issue 1, Pages 5-10 (January 2008).
Etanercept, from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Figures:
What are some of the treatment options for such patients?
- Anti-IgE. Omalizumab (Xolair). Omalizumab binds to Cε3 region of IgE. Oral corticosteroids were withdrawn in 74% of severe asthma patients treated with omalizumab - Current Medical Research and Opinion, 2010.
- Anti-TNF-α
Etanercept (Enbrel)
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a proinflammatory cytokine that has been implicated in the airway pathology in asthma. TNF-α may play an important role in severe refractory asthma.
Preliminary studies with anti–TNF-α therapy look promising but there is a marked heterogeneity in response, suggesting that benefit is likely to be reserved to a small subgroup. The long-term safety of anti–TNF-α therapy is also uncertain.
Etanercept (Enbrel) is a recombinant human TNF-α receptor fusion protein (anti-TNF-α). Its therapeutic potential is based on the fact that TNF-alpha is the "master regulator" of the inflammatory response in many organ systems.
Etanercept is a large molecule that binds to TNF-α and decreases its role in disorders involving excess inflammation such as:
- ankylosing spondylitis
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- psoriasis
- psoriatic arthritis

Mediators from Eosinophils. TNF-α is one of them.

Asthma classification and treatment for each stage. See more Allergy and Immunology mind maps here.
Severe asthma - differential diagnosis and management (click to enlarge the image).
References:
Targeting TNF-α: A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. JACI, Volume 121, Issue 1, Pages 5-10 (January 2008).
Etanercept, from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Response to omalizumab after 16 weeks is a predictor of continuing persistent response to omalizumab in asthmatics. Allergy 2011.
Images: Mechanisms of action of omalizumab. JACI, 02/2008.
Images: Mechanisms of action of omalizumab. JACI, 02/2008.
Figures: